Hypothyroidism and obesity are two separate medical conditions, but they are often interrelated. Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, is not producing enough thyroid hormone.
This hormone is responsible for regulating the body’s metabolism, which is the process of converting food into energy. When there is not enough thyroid hormone, the metabolism slows down, which can lead to weight gain.
Obesity is defined as having an excessive amount of body fat. It is usually determined by calculating the body mass index (BMI), which is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. A BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese.
Obesity and hypothyroidism are related in that individuals with hypothyroidism are at a higher risk of becoming obese.
The slowed metabolism caused by hypothyroidism can make it more difficult to lose weight and keep it off. Additionally, obesity can also contribute to the development of hypothyroidism by making it more difficult for the thyroid gland to function properly.
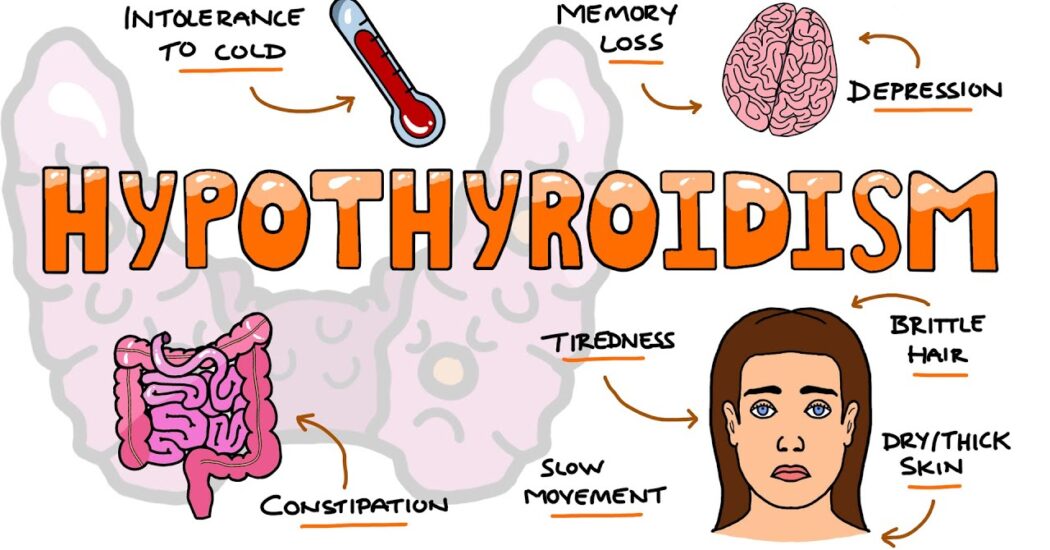
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, dry skin, depression, and muscle weakness.
Symptoms of obesity include excessive weight gain, difficulty losing weight, and increased risk of developing chronic health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
Treatment of hypothyroidism typically involves taking a daily thyroid hormone replacement medication, such as levothyroxine.
This medication replaces the thyroid hormone that the body is not producing enough of. In addition, it is important to maintain a healthy diet and engage in regular physical activity to help manage weight gain and improve overall health.
Treatment of obesity typically involves a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. A healthcare professional can help develop a personalized plan that is tailored to your needs and goals.
This plan may include recommendations for specific types of physical activity, changes in diet, and other lifestyle changes that can help you lose weight and maintain a healthy weight over time.
In summary, hypothyroidism and obesity are two separate medical conditions, but they are often interrelated. Individuals with hypothyroidism are at a higher risk of becoming obese, and obesity can also contribute to the development of hypothyroidism. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop an appropriate plan to manage both conditions and improve overall health.




